First Degree Atrioventricular Block
Related articles: AV blocks, second degree AV block, complete AV block.
First degree AV block is the mildest atrioventricular block.
In this AV block there is a delay in the conduction of the electrical impulse within the AV node or the His-Purjinke system, causing a PR interval greater than 200 ms 1.
In first degree AV block, the conduction disorder is usually produced in the atrioventricular node, and more rarely, in the His-Purkinje system (read cardiac conduction system).
Electrocardiogram Findings of First Degree AV Block
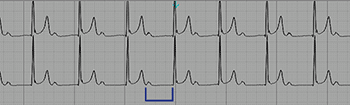
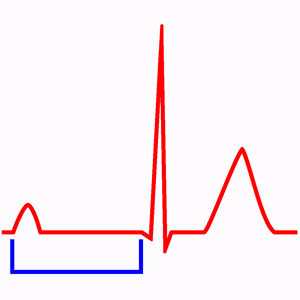
First degree AV block with prolonged PR interval (0.52 sec).
The electrocardiogram is characterized by P waves followed by normal QRS complexes, but with prolonged PR interval of 0.20 s or higher (1 large square).
In first degree AV block the stimulus is always conducted to the ventricles, so, all P waves are followed by a QRS complex (unlike other AV blocks).
In some patients, the PR interval is so prolonged, that the P wave appears included in the previous QRS or even before it.
Electrocardiogram of First Degree AV Block
- Prolonged PR interval, >0.20 seconds (1 large square).
- All P waves are followed by a QRS complex.
- Normal QRS pattern, if no other alteration is present.
Presentation and Treatment of First Degree AV Block
The first degree atrioventricular block is usually asymptomatic and do not produce changes in heart function 2.
Antiarrhythmic drugs can cause first degree AV block, if so, should assess the risk/benefit of continuing treatment. It also appears in hyperkalemia.
When there is a markedly prolonged (>0.3 s) PR interval, atrioventricular dyssynchrony may occur and may appear symptoms, especially during exercise.
The first degree atrioventricular block does not require pacemaker implantation.
Although patients with very prolonged PR interval with symptoms during exercise could need the implantation of a DDD pacemaker to ensure atrioventricular synchrony.
The finding of a first degree AV block with a bifascicular block can mean important conduction system disease and, if it is accompanied by symptoms, is usually an indication of permanent pacemaker implantation.
Related articles: AV blocks, second degree AV block, complete AV block.
References
- 1. Castellano C, Pérez de Juan MA, Attie F. Electrocardiografía Clínica, 2ª Ed. Madrid: Elservier España S. A. ; 2004.
- 2. Surawicz B, Knilans TK. Chou’s electrocardiography in clinical practice, 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elservier; 2008.
- 3. Vogler J, Breithardt G, Eckardt L. Bradyarrhythmias and Conduction Blocks. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2012;65(7):656–667. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2012.01.027
If you Like it... Share it.