What is a Holter EKG?
The electrocardiogram holter, also called EKG holter or heart rate holter, is a device that allows the monitoring of the heart rhythm for a given time, usually 24 hours.
It takes its name from the biophysicist Norman J. Holter, who invented continuous cardiac monitoring.
The main purpose of this device is to continuously record a patient's electrocardiogram over a prolonged period of time.
What is a Holter ECG?
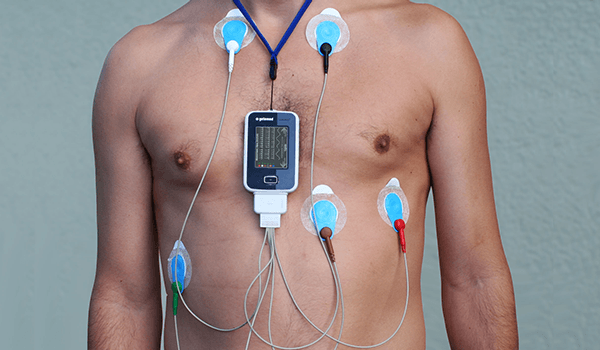
The EKG holter consists of a device that stores the information, connected to the patient by means of electrodes (usually between 4 and 5 in a standard holter).
Once the test has been performed, the device is connected to a computer to obtain the information and analyze the results.
¿Cómo se realiza un Holter EKG?
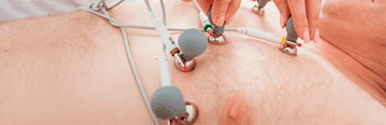
The procedure consists of placing the electrodes on the patient's chest, in positions different from those used in a standard EKG.
In order to avoid disconnections during recording and to ensure the stability of the electrodes, they are usually fixed with adhesive tape.
The patient should go about his or her normal life during the monitoring period, except for taking a shower or getting the device wet.
After 24 to 48 hours the patient should return to the center where it was placed to remove the equipment and proceed to its analysis.
Rhe report with the results of the holter is usually delivered several days after it has been performed.
Differences Between a Holter and a Standard EKG
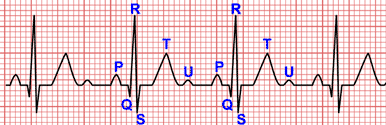
The main difference between a holter and a standard electrocardiogram lies in the reading time.
An EKG usually measures about 6 seconds of cardiac electrical activity, while the holter generally records 24 to 48 hours of activity.
Another significant difference is the number of leads.
While a standard EKG has 12 leads, most holter devices usually have 2 or 3 leads, although 12-lead holters are now available.
What is the Purpose of the Holter EKG?
The main objective of the holter is the diagnosis of arrhythmias, especially those that are difficult to detect in a standard electrocardiogram due to their sporadic nature.
This makes this device a very useful tool for the study of syncope, frequent palpitations, dizziness, among others.
In addition, it is used to monitor patients with known arrhythmias, either to evaluate the efficacy of medical or interventional treatment.
It is also used in patients with ischemic stroke without an identified cause, for the possible presence of undiagnosed paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
Holter EKG can help to suspect ischemic heart disease by detecting variations in the ST segment during the test, although more specific additional tests are required to confirm this diagnosis.
The ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (BP holter or ABPM) and the 24-hour ambulatory electroencephalogram (EEG holter) are also called holter.
Implantable Holter
The implantable holter is a small device that is implanted under the skin in the upper chest area.
The surgical procedure to implant this holter is simple, is performed under local anesthesia and has few complications.
This device continuously records the heart's activity automatically or with a manual trigger throughout its useful life, which is currently usually 3 years.
If you Like it... Share it.