How to Know if an Electrocardiogram is Performed Correctly
The first step to assess when reading an electrocardiogram is to determine if the EKG is well performed.
Sometimes, due to lack of knowledge, haste or carelessness, mistakes are made when performing an electrocardiogram.
It is our duty, as professionals, to recognize these errors, repeat the EKG if possible and clarify our colleagues' doubts about how to perform it correctly.
Below we will discuss the details to know if an electrocardiogram is correctly performed.
Identify with name, date and time
Name:
Not placing the patient's name is one of the most frequent errors when performing an electrocardiogram.
Imagine on the table three electrocardiograms of three different patients with no name or identification, how can you know whose they are, if you add to that medical records, analytical and a few more papers, you would have to have an incredible memory to remember who they belong to.
Date and time:
This is very important to determine when an EKG alteration has occurred. Especially in patients with ischemic heart disease or arrhythmias.
In order to determines when there have been significant changes in an EKG, it is essential that these have the date and time when it was performed.
A well-performed electrocardiogram should have the patient's name, date and time when it was performed.
The 12 leads are well recorded
For an electrocardiogram to be considered well performed, all 12 leads must be well recorded, as they are essential for the correct analysis of an EKG.
It is frequent that a lead does not register electrical activity or the presence of many electrical artifacts due to a bad connection of an electrode. When this happens, the electrode should be correctly positioned and the EKG repeated.
Another common mistake is to only perform a rhythm or long strip EKG, which consists of fewer leads than the standard EKG.
This type of EKG is an excellent tool to evaluate the heart rhythm over a longer period of time, but a 12-lead EKG should always be performed to complete the study.
A well-performed EKG should have all 12 leads well recorded.
Presence of few artifacts on the EKG
Artifacts are signals external to the heart recorded on the electrocardiogram. The most frequent artifacts are those produced by movements or by poor contact of an electrode with the skin.
The presence of a few isolated artifacts does not hinder a correct reading of an electrocardiogram, but several of them or a very artifactual EKG can lead to diagnostic errors.
Therefore, if there are many artifacts in an EKG, it should be repeated.
A well-performed EKG should have as few artifacts as possible.
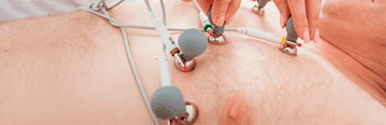
Correctly positioned electrodes
One of the most frequent errors when performing an electrocardiogram is to place the electrodes incorrectly (see electrode placement).
We remind you that each electrode has a different color, to make it easier to differentiate between them.
Limb leads reversal
It is common to reverse the electrodes on the arms and legs, causing changes in the peripheral leads.
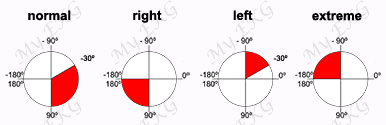
The simplest way to recognize a leads reversal is to observe the aVR lead. In this lead the P wave, QRS complex and T wave should be predominantly negative, except in rare situations.
Another alteration that allows us to suspect a limb leads reversal is to observe negative P waves in lead I with a right axis deviation, this usually translates a left and right arm leads reversal.
When there is an extreme axis deviation and all waves, including the P wave, are negative in lead aVF, a right arm and left leg leads reversal should be suspected.
The surest method to determine that the electrodes are properly placed is Einthoven's law, which tells us that the net amplitude of the QRS complex in lead II is equal to the sum of the net amplitudes of the QRS complexes of I and III (II = I + III). If this is not met, the peripheral electrodes have been misplaced.
Misplacement of precordial leads:
Placing precordial electrodes at very low or very high positions is even more common than a limb leads reversal.
This causes changes in the morphology of the QRS complexes in the precordial leads, changes that are much more difficult to notice than those described above, so correct electrode placement must be insisted upon.
To ensure that an electrocardiogram is properly performed, the correct placement of the electrodes should be checked.
Summary
To determine if an EKG is properly performed, it is necessary to check the following steps.
- Patient's name, date and time when it was performed.
- All 12 leads well recorded.
- The minimum possible artifacts.
- Check the correct placement of the electrodes.
We hope this post on how to know when an electrocardiogram is well done has been of interest to you.
If you Like it... Share it.