Second Degree Atrioventricular Block
Related articles: AV blocks, first degree AV block, complete AV block.
With second-degree AV block an intermittent failure of the AV conduction occurs. Not all P waves are followed by a QRS complex, causing pauses in ventricular stimulation.
There are two types of second-degree AV block, type I, also called Mobitz type I or Wenckebach phenomenon, and type II, also called Mobitz type II.
This article will also discuss the second-degree AV block with conduction ratio 2:1 and advanced AV block.
Type I Second Degree AV Block. Mobitz type I or Wenckebach Phenomenon
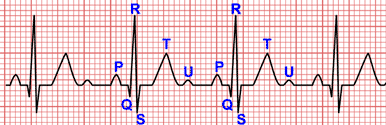
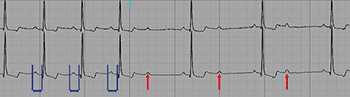
In type I second-degree atrioventricular block (Wenckebach phenomenon) there is an AV conduction block with a progressive lengthening of PR interval of previous beats.
In other words: there is a progressive PR interval lengthening until a P wave is not conducted (Wenckebach phenomenon). Progressive shortening of the RR interval until a blocked P wave is also observed.

Type I second-degree AV block (Wenckebach phenomenon): Progressive lengthening of the PR interval until a P wave is blocked (red).
Electrocardiogram Findings
- Progressive lengthening of the PR interval until a P wave is not followed by a QRS complex (blocked P wave).
- Progressive shortening of the RR interval until a P wave is blocked.
- RR interval containing the blocked P wave is shorter than the sum of two PP intervals 1.
Prolongation of the PR interval may not be progressive. If previous PR intervals are different from each other, it is also considered type I second-degree atrioventricular block 1 2.
At least two consecutive PR intervals are needed before the blocked P to determine the type of AV block.
Type I second-degree AV block is considered benign and is usually asymptomatic. In most patients there is no progression to more serious AV blocks. In elderly patients closer monitoring is recommended.
Type II Second-Degree AV Block. Mobitz type II
Type II second-degree AV block or Mobitz type II is less frequent, and almost always means severe disease of the conduction system 3.
It differs from the type I second-degree AV block by constant PR intervals, before and after the blocked P wave.
Electrocardiogram Findings
- Constant PR intervals before and after the blocked P wave.
- The PR interval after the blocked P waves is similar to the previous PR interval.
- RR interval containing the blocked P wave is similar to the sum of two PP intervals.
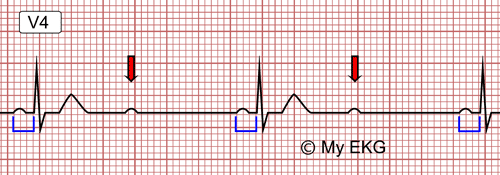
Type II second-degree AV block, Mobitz type II:
Constant PR before blocked P. Last beats with AV conduction ratio 2:1.
In second-degree AV block Mobitz type II, is usually located distal to bundle of His, especially if it is associated with bundle branch block 1.
Type II second-degree AV block may require pacemaker therapy for prognostic reasons and pacing may be indicated in asymptomatic patients 4.
2:1 Second-Degree AV Block
In 2:1 AV block the conduction ratio is 2:1, alternating a conducted P wave with a blocked P wave.
In the absence of two consecutive PR intervals is impossible to determine if the second degree AV block is type I or II, because is not possible to determine whether the PR varies 1.
2:1 second-degree AV block
Alternating conducted P waves with blocked P waves (red). PR intervals of conducted P waves is constant.
A long rhythm strip or 24 hours holter monitor may help to determine the type of block. Although occasionally is necessary an electrophysiological study.
High-grade or Advance Second-Degree AV Block
In advance second-degree AV block there are more than one consecutive blocked P wave, conduction ratio 3:1 or more.
Identifying the type of second-degree AV block in such instances is also difficult. A comparison of the PR intervals of the occasional captured complexes may help 1.
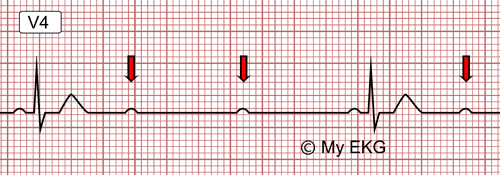
Advance second-degree AV block:
After a conducted P wave, there are two blocked P waves (red arrows)
This type of AV block has higher risk and poorer prognosis than previous ones, and can cause severe episodes of symptomatic bradycardia.
Advance AV block usually requires electronic pacemaker implantation.
Related articles: AV blocks, First degree AV block, complete AV block.
References
If you Like it... Share it.