Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block
Incomplete left bundle branch block implies slowing of conduction in the left bundle branch, causing the left ventricle to be partially activated from the right bundle branch 1 2.
It is defined by QRS complex duration between 110 and 119 ms in adults, R peak time greater than 60 ms in leads V4, V5, and V6 and absence of Q wave in leads I, V5, and V6.
EKG of Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block
Incomplete left bundle branch block is less common than complete left bundle branch block 3.
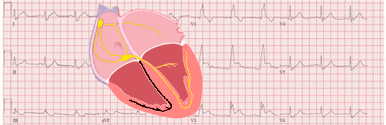
The initial depolarization of the left ventricle occurs via impulses spreading from the right ventricle, but after a while the impulse passes the block in the left bundle branch and executes the remaining ventricular depolarization 3.
Hence, the initial QRS complex resembles left bundle branch block, but QRS complex is not longer than 120 ms.
EKG Criteria of Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block
From Surawicz B, Deal BJ et al. AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram Part III: Intraventricular Conduction Disturbances 2.
- QRS complex duration between 110 and 120 ms in adults, between 90 and 100 ms in children between 4 and 16 years of age, and between 86 and 90 ms in children less than 4 years of age.
- Presence of left ventricular hypertrophy pattern.
- R peak time greater than 60 ms in leads V4, V5, and V6.
- Absence of Q wave in leads I, V5, and V6.
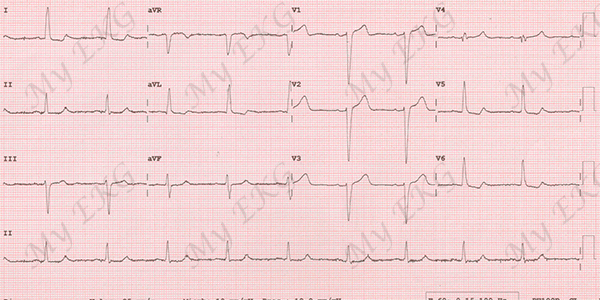
Incomplete left bundle branch block:
QRS complex <120 ms, R peak time greater than 60 ms in left precordial leads, and absence of Q wave in leads I, V5, and V6.
The presence of notching or slurring, or both, of the ascending limb of the R wave in the left precordial leads increases the likelihood of the diagnosis of incomplete left bundle branch block 1 4.
The presence of incomplete left bundle branch block should be suspected when the EKG shows a pattern of left ventricular hypertrophy with slight QRS widening and absent Q waves in the left precordial leads and lead I 2 3.
Causes of Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block
Ischemic heart disease and left ventricular hypertrophy are the two most common clinical and anatomic entities associated with the incomplete left bundle branch block 5.
It is appropriate to view the pattern of incomplete left bundle branch block as a variant of left ventricular hypertrophyy pattern with additional conduction delay but with similar secondary ST-segment and T wave changes 2.
References
- 1. Willems JL, Robles de Medina EO, et al Criteria for intraventricular conduction disturbances and pre-excitation. JACC. 1985; 5(6): 1261-1275. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(85)80335-1.
- 2. Surawicz B, Deal BJ et al. AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram Part III: Intraventricular Conduction Disturbances. Journal of the American College of Cardiology Mar 2009, 53(11): 976-981. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.12.013.
- 3. Pérez-Riera AR, Barbosa-Barros R. Left bundle branch block: Epidemiology, etiology, anatomic features, electrovectorcardiography, and classification proposal. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019 Mar; 24(2): e12572. doi: 10.1111/anec.12572.
- 4. Sodi-Pallares D, Estandía A, et al. The left intraventricular potential of the human heart: II. Criteria for diagnosis of incomplete bundle branch block. American Heart Journal. 1950; 40(5): 655-679. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(50)90198-0.
- 5. Wasserburger RH, White DH, Lindsay ER. The Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block. Chest. 1963; 43(6): 594–600. doi: 10.1378/chest.43.6.594.
If you Like it... Share it.