Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block
Incomplete right bundle branch block is a common finding at all ages with more prevalence in men compared with women 1.
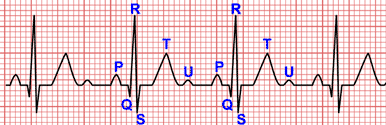
It is defined by QRS complex duration between 110 and 120 ms in adults and a rsr', rsR', or rSR' pattern in leads V1 or V2 2, and it implies a partial block in the right Purkinje system.
EKG Criteria of Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block
From Surawicz B, Deal BJ et al. AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram Part III: Intraventricular Conduction Disturbances 2.
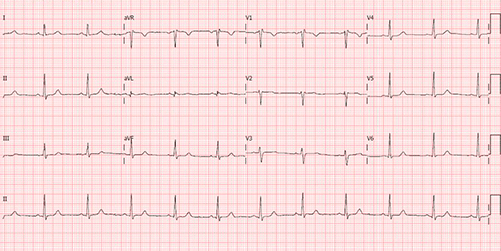
Incomplete right bundle branch block:
QRS complex <120 ms, rSR' pattern in leads V1 and V2. R' wave is than the initial R wave.
- QRS complex duration between 110 and 120 ms in adults, between 90 and 100 ms in children between 4 and 16 years of age, and between 86 and 90 ms in children less than 4 years of age.
- rsr', rsR', or rSR' pattern in leads V1 or V2. The R' or r' wave is usually wider than the initial R wave.
Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block in Adult Population
The prevalence of incomplete RBBB in the adult population is estimated to be 5% to 10%, and it tends to increase with advancing age 3, with higher prevalence in people with lower body mass index 1.
The presence of incomplete RBBB is not related to cardiovascular diseases risk factors 1.
Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block in Athletes
Related article: Normal EKG findings in athletes.
The prevalence of incomplete right bundle branch block has been estimated to range from 35 to 50% in athletes, and this EKG pattern is more often noted in athletes engaged in endurance sports 4.
It has been suggested that the right ventricular conduction delay is not within the specialized conduction system, but is caused by the enlarged right ventricular cavity size or increased cardiac muscle mass and the resultant increased conduction time 4.
The incomplete RBBB patern has been shown to be reversible with deconditioning 4.
More information: Normal EKG findings in athletes.
Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block in Pediatric Population
The rsr', rsR', or rSR' pattern with a normal QRS complex duration in leads V1 and V2 is a normal variant in children of any age 2 3.
Incomplete right bundle branch block is defined by QRS complex duration between 90 and 100 ms in children between 4 and 16 years of age, and between 86 and 90 ms in children less than 4 years of age 2.
Incomplete RBBB may be diagnosed when the terminal rightward deflection is less than 40 ms but greater than or equal to 20 ms 2.
Once structural and functional cardiac anomalies have been ruled out, incomplete RBBB does not have much clinical significance in the pediatric population 3.
Causes of Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block
Congenital Heart Disease
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
Other Causes of Incomplete Right Bundle Branch Block
- Loeffler endocarditis
- Chagas disease
- Heart transplantation
- Drugs
Some Recommendations for Incomplete RBBB
Incomplete RBBB does not require further evaluation in the presence of a negative family/personal history and physical examination 1 3 4, but in the presence of some clinical findings other heart diseases should be suspected.
Atrial Septal Defect
Because incomplete RBBB is a typical EKG finding in patients with an ostium secundum atrial septal defect (ASD), symptoms and a fixed split of the second heart sound on auscultation should be excluded 4.
Normal axis or right-axis deviation and incomplete RBBB are the most commonly observed EKG findings in patients of ostium secundum atrial septal defect.
Incomplete right bundle branch block alone is inadequate to diagnose ASD.
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy should be suspected when the pattern of incomplete RBBB is associated with T-wave inversion extending beyond V2 to include leads V3 and V4, or in the presence of premature ventricular beats with a left bundle branch block morphology 4.
Summary
Incomplete right bundle branch block is a common finding at all ages with more prevalence in males and athletes 1 4.
In adults, it is defined by QRS duration between 110 and 120 ms and a rsr', rsR', or rSR' pattern in leads V1 or V2 2.
Incomplete RBBB does not require further evaluation if there is a negative family/personal history and physical examination 1 3 4.
In the presence of some clinical findings other heart diseases should be ruled out.
References
- 1. Bussink BE, Holst AG et al. Right bundle branch block: prevalence, risk factors, and outcome in the general population: results from the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Eur Heart J; 2013; 34: 138–146. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs291.
- 2. Surawicz B, Deal BJ et al. AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram Part III: Intraventricular Conduction Disturbances. Journal of the American College of Cardiology Mar 2009; 53 (11): 976-981. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.12.013.
- 3. Park M. Electrocardiography. In: Pediatric Cardiology for Practitioners. Philadelphia, Elsevier. 2014: 41-66.
- 4. Corrado D, Pelliccia A et al. Recommendations for interpretation of 12-lead electrocardiogram in the athlete. Eur Heart J 2009; 31: 243–59. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp473.
If you Like it... Share it.