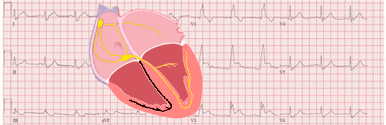
PR Interval
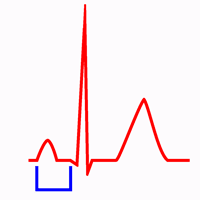
The PR interval is measured from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex. It comprises the P wave and the PR segment.
The interval should be measured in the lead with the largest, widest P wave and the longest QRS duration 1.
The PR interval includes the atrial depolarization and the propagation of the impulse through the AV node and the Conduction System until the ventricular myocardium begins to depolarize 1.
It does not include the duration of conduction from the Sinus Node to the right atrium (Sinoatrial conduction).
The PR interval also includes the atrial repolarization (atrial T wave), which is directed opposite to the P wave axis, but atrial repolarization usually has low amplitude and the PR segment is frequently isoelectric 1.
Normal and Abnormal PR Interval
Normal PR Interval:
In adults the normal PR interval is 0.12 s to 0.20 s (3 to 5 small squares).
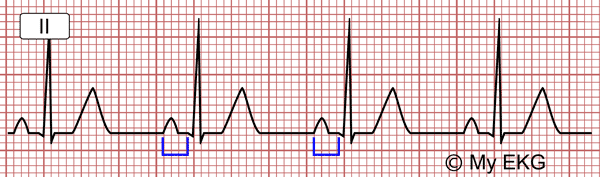
Normal PR interval (0.14 s).
It is generally shorter in children (see pediatric EKG) and in pregnant women, and it is longer in older persons.
Prolonged PR Interval:
Prolongation of the PR interval above 0.20 s (5 small squares) is called first degree AV block.
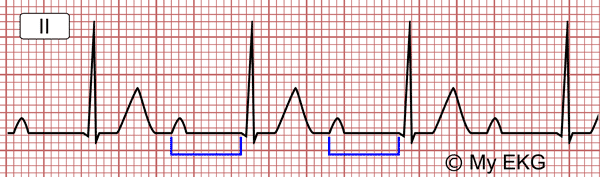
First degree AV Block with prolonged PR interval (0.36 sec).
It indicates a conduction delay from the sinus node to the ventricles. The atrioventricular node is the most commonly involved site in adults.
In type I 2nd degree AV block there is a progressive PR lengthening until a P wave is not conducted (Wenckebach phenomenon).
Short PR Interval
A short PR interval (<0.12 sec) may be caused by a pre-excitation syndrome (Wolff-Parkinson-White), ectopic atrial pacemaker or AV junctional rhythm.
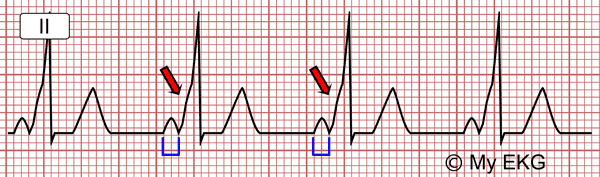
Wolff-Parkinson-White with short PR interval (0.08 sec) and delta wave (red arrows).
The most important findings in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are a short PR interval, the presence of the delta wave and wide QRS complex.
In ectopic atrial pacemaker or AV junctional rhythm may be seen a short PR interval with an abnormal P waves with narrow QRS complex.
Elements of the PR Interval
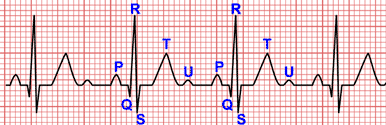
P Wave
Related articles: EKG waves, abnormal waves and intervals.
The P wave represents atrial depolarisation, it is the result of overlaying the electrical activity of both atria.
P wave duration is less that 0.10 s and its maximum voltage is 0.25 mV. Normal P wave is positive in all leads except aVR where it is negative, and V1, where P wave is biphasic.
More information: EKG waves, abnormal waves and intervals.
PR Segment
Related article: Segments and intervals.
PR segment is the isoelectric segment between the end of the P wave and the start of the QRS complex. It is included in the PR interval (read difference between segments and intervals).
Causes of PR Segment Depression:
- Exercise-induced tachycardia.
- Presences of taller P waves.
- Acute pericarditis.
- Atrial ischemia.
More information: Segments and intervals.
We hope we have been able to help you with the PR interval. For further details on the analysis of QT interval, click Next.
previous | next
References
- 1. Surawicz B, Knilans TK. Chou’s electrocardiography in clinical practice, 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elservier; 2008.
If you Like it... Share it.