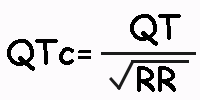PR Interval
Related Article: PR Interval.
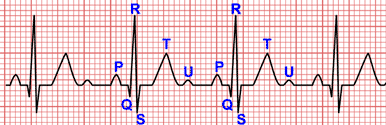
The PR interval is measured from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex.
Electrically speaking, it covers atrial depolarization and the propagation of the the stimulus through the AV Node and the Bundle of Hiss.
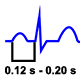
Normal PR Interval: The normal PR measure is greater than 0.12 s and less than 0.20 s (120 to 200 ms).
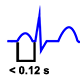
Short PR interval: If the PR is less than 0.12 s indicates accelerated atrioventricular conduction. The most obvious example is the Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome.
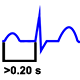
Long PR Interval: If the PR is greater than 0.20 s indicates delayed atrioventricular conduction. It is frequent in AV Node disorders.
More Information: PR Interval.
QT Interval
Related Article: QT Interval.
The QT Interval represents electrical systole of the ventricles (Ventricular depolarisation and repolarisation). It is measured from the beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave.
The QT interval varies depending on hear rate, so to determine whether is normal or not, it must be corrected.
The heart rate-corrected QT (QTc) interval is the one a patient would have at 60 bpm, and to estimate it, the Bazett’s formula is used.
Prolonged QTc Interval
QTc intervals are pathological if greater than 460 ms in children under the age of 15, 450 ms in men, and 470 ms in women.
Short QTc Interval
Diagnostic criteria for Short QT syndrome are not entirely defined because it is a new clinical entity, described in 2000.
A QTc interval less than 340 ms is usually accepted as pathological.
More Information: QT Interval
We hope we have been able to help you. For further details on How to determine the Electrical Axis, click Next.